Toolkit Contributors and Users
Building the Toolkit is a global, community effort and the fruits of that work are used even more widely. The below map shows the location of the developers, contributors and users of the Toolkit.
The location of the lead institutions are shown in red, contributors are shown in blue and users in yellow. If you fall into any of these categories and are missing from the map let us know so we can add you.
Papers that acknowledge, cite and/or extend the Toolkit
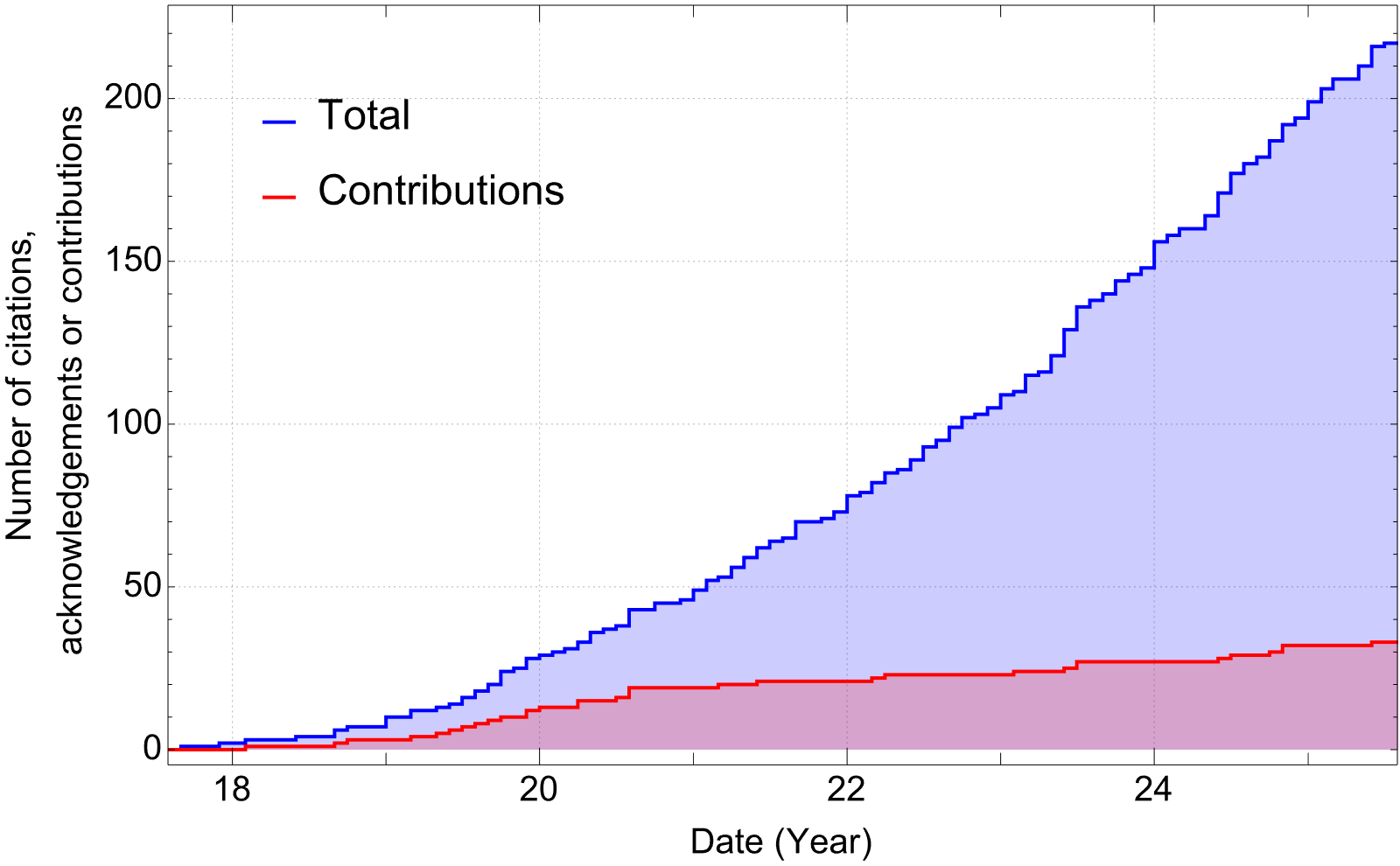
The graph below show the accumulated citations to the Toolkit over time. The blue curve shows the total citations and acknowledgements, the red curve tracks the total number of papers that have contributed software or data to the Toolkit.
Below is a list of research papers that have used or extended the Toolkit. Papers that have contributed code or data to the Toolkit have a (*) after them.
261. “Bayesian inference for tidal heating with extreme mass ratio inspirals”, Zhong-Wu Xia, Sheng Long, Qiyuan Pan, Jiliang Jing, Wei-Liang Qian, arXiv:2602.11039
260. “Resummed energy loss in extreme-mass-ratio scattering using critical orbits”, Leor Barack, Riccardo Gonzo, Benjamin Leather, Oliver Long, Niels Warburton, arXiv:2602.10089
259. “Probing Quantum Gravity effects with Extreme Mass Ratio Inspirals around Rotating Hayward Black Holes”, Dan Zhang, Chao Zhang, Qiyuan Pan, Guoyang Fu, Jian-Pin Wu, arXiv:2602.07436
258. “The gravitational Compton amplitude at third post-Minkowskian order”, N. Emil J. Bjerrum-Bohr, Gang Chen, Carl Jordan Eriksen, Nabha Shah, arXiv:2602.06947
257. “Gravitational Wave Scattering in Spinless WQFT”, Yilber Fabian Bautista, Mathias Driesse, Kays Haddad, Gustav Uhre Jakobsen, arXiv:2602.06125
256. “Decomposition of Schwarzschild Green’s Function”, Junquan Su, Neev Khera, Marc Casals, Sizheng Ma, Abhishek Chowdhuri, Huan Yang, arXiv:2601.22015
255. “Spiral Density Waves and Torque Balance in the Kerr Geometry”, Conor Dyson, Daniel J. D’Orazio, arXiv:2601.19123
254. “Constants of motion in gravitational self-force theory”, David Trestini, Zachary Nasipak, Adam Pound, arXiv:2601.05223
253. “Quasinormal mode/grey-body factor correspondence for Kerr black holes”, Zun-Xian Huang, Peng-Cheng Li, arXiv:2512.23510
252. “The evaporation of near-extremal black holes through charged particle emission”, Ilija Rakic, arXiv:2512.18895
251. “Quasinormal modes of rotating black holes beyond general relativity in the WKB approximation”, Ruijing Tang, Nicola Franchini, Sebastian H. Völkel, Emanuele Berti, arXiv:2512.17786
250. “Inspiral-Transition-Plunge Gravitational Waveforms Beyond Kerr: A Kerr-Newman Case Study”, Daiki Watarai, Kent Yagi, Shammi Tahura, arXiv:2512.14156
249. “Quasinormal ringing of Kerr black holes. III. Excitation coefficients for equatorial inspirals from the innermost stable circular orbit”, Matteo Della Rocca, Laura Pezzella, Emanuele Berti, Leonardo Gualtieri, Andrea Maselli, arXiv:2512.07959
248. “Gravitational radiation from hyperbolic orbits: comparison between self-force, post-Minkowskian, post-Newtonian, and numerical relativity results”, Niels Warburton, arXiv:2512.02274
247. “Scattering of charged massive scalar waves by Kerr-Newman black holes”, Qian Li, Qianchuan Wang, Junji Jia, arXiv:2511.21318
246. “Constraint on massive vector field with extreme-mass-ratio inspirals around a slowly rotating black hole”, Tieguang Zi, Peng-Cheng Li, Bao-Min Gu, Fu-Wen Shu, arXiv:2511.18435
245. “The Physics of Black Holes and Their Environments: Consequences for Gravitational Wave Science”, Vitor Cardoso, Shauvik Biswas, Subhodeep Sarkar, arXiv:2511.14841
244. “Sub-Solar Mass Intermediate Mass Ratio Inspirals: Waveform Systematics and Detection Prospects with Gravitational Waves”, Devesh Giri, Bhooshan Gadre, arXiv:2511.13324
243. “Black-hole scattering with numerical relativity: Self-force extraction and post-Minkowskian validation”, Oliver Long, Harald P. Pfeiffer, Lawrence E. Kidder, Mark A. Scheel, arXiv:2511.10196
242. “Gravitational radiation from Kerr black holes using the Sasaki-Nakamura formalism: waveforms and fluxes at infinity”, Yucheng Yin, Rico K. L. Lo, Xian Chen, arXiv:2511.08673
241. “A-BHPT-toolkit: Analytic Black Hole Perturbation Theory Package for Gravitational Scattering Amplitudes”, Jovan Markovic, Mikhail M. Ivanov, arXiv:2511.04765
240. “Eccentric extreme-mass-ratio inspirals: a new window into ultra-light vector fields”, Tieguang Zi, Fu-Wen Shu, arXiv:2510.22275
239. “Ab uno disce omnes: Single-harmonic search for extreme mass-ratio inspirals”, Lorenzo Speri, Rodrigo Tenorio, Christian Chapman-Bird, Davide Gerosa, arXiv:2510.20891
238. “Hybrid waveform model for asymmetric spinning binaries: Self-force meets post-Newtonian theory”, Loïc Honet, Adam Pound, Geoffrey Compère, arXiv:2510.16114
237. “Post-adiabatic self-force waveforms: slowly spinning primary and precessing secondary”, Josh Mathews, Barry Wardell, Adam Pound, Niels Warburton, arXiv:2510.16113
236. “Spin-aligned inspiral waveforms from self-force and post-Newtonian theory”, Loïc Honet, Josh Mathews, Geoffrey Compère, Adam Pound, Barry Wardell, Gabriel Andres Piovano, Maarten van de Meent, Niels Warburton, arXiv:2510.16112
235. “Transition-to-plunge self-force waveforms with a spinning primary”, Loïc Honet, Lorenzo Küchler, Adam Pound, Geoffrey Compère, arXiv:2510.13958
234. “Black hole mergers beyond general relativity: a self-force approach”, Ayush Roy, Lorenzo Küchler, Adam Pound, Rodrigo Panosso Macedo, arXiv:2510.11793
233. “Hybridization of second-order gravitational self-force and numerical relativity waveforms for quasi-circular and non-spinning black hole binaries”, Hector Iglesias, Leanne Durkan, Deirdre Shoemaker, arXiv:2510.11685
232. “Particles with precessing spin in Kerr spacetime: analytic solutions for eccentric orbits and homoclinic motion near the equatorial plane”, Gabriel Andres Piovano, arXiv:2510.09597
231. “A relativistic treatment of accretion disk torques on extreme mass ratio inspirals around spinning black holes”, Abhishek Hegade K.R., Charles F. Gammie, Nicolás Yunes, arXiv:2510.03564
230. “Consistency of spin effects between numerical relativity and perturbation theory for inspiraling comparable-mass black hole binaries”, Tousif Islam, Gaurav Khanna, Scott E. Field, arXiv:2510.00531
229. “A relativistic treatment of accretion disk torques on extreme mass-ratio inspirals around non-spinning black holes”, Abhishek Hegade K. R., Charles F. Gammie, Nicolás Yunes, arXiv:2509.20457
228. “Systematic errors in fast relativistic waveforms for Extreme Mass Ratio Inspirals”, Hassan Khalvati, Philip Lynch, Ollie Burke, Lorenzo Speri, Maarten van de Meent, Zachary Nasipak, arXiv:2509.08875
227. “Resonance in black hole ringdown: Benchmarking quasinormal mode excitation and extraction”, Kei-ichiro Kubota, Hayato Motohashi, arXiv:2509.06411
226. “Prospects for EMRI/MBH parameter estimation using Quasi-Periodic Eruption timings: short-timescale analysis”, Joheen Chakraborty, Lisa V. Drummond, Matteo Bonetti, Alessia Franchini, Shubham Kejriwal, Giovanni Miniutti, Riccardo Arcodia, Scott A. Hughes, Francisco Duque, Erin Kara, Alberto Sesana, Margherita Giustini, Amedeo Motta, Kevin Burdge, arXiv:2508.20162
225. “Emergent Turbulence in Nonlinear Gravity”, Sizheng Ma, Luis Lehner, Huan Yang, Lawrence E. Kidder, Harald P. Pfeiffer, Mark A. Scheel, arXiv:2508.13294
224. “Effective source for second-order self-force calculations: quasicircular orbits in Schwarzschild spacetime”, Samuel D. Upton, Barry Wardell, Adam Pound, Niels Warburton, Leor Barack, arXiv:2508.00087
223. “Gravitational Wave Peep Contributions to Background Signal Confusion Noise for LISA”, Daniel J Oliver, Aaron D Johnson, Lena Janssen, Joel Berrier, Kostas Glampedakis, Daniel Kennefick, arXiv:2507.19704
222. “Towards relativistic inspirals into black holes surrounded by matter”, Lukáš Polcar, Vojtěch Witzany, arXiv:2507.15720
221. “A New High-Performing Method for Solving the Homogeneous Teukolsky Equation”, Ye Jiang, Wen-Biao Han, arXiv:2507.15363
220. “Post-adiabatic waveforms from extreme mass ratio inspirals in the presence of dark matter”, Mostafizur Rahman, Takuya Takahashi, arXiv:2507.06923
219. “Post-Newtonian expansion of fluxes from a scalar charge on an inclined-spherical orbit about a Kerr black hole”, Jezreel C. Castillo, Charles R. Evans, Chris Kavanagh, Jakob Neef, Barry Wardell, Adrian Ottewill, arXiv:2507.07303 (*)
218. “Peaking into the abyss: Characterizing the merger of equatorial-eccentric-geodesic plunges in rotating black holes”, Guglielmo Faggioli, Maarten van de Meent, Alessandra Buonanno, Gaurav Khanna, arXiv:2507.05870
217. “Extreme mass-ratio inspiral within an ultralight scalar cloud I. Scalar radiation”, Dongjun Li, Colin Weller, Patrick Bourg, Michael LaHaye, Nicolás Yunes, Huan Yang, arXiv:2507.02045
216. “Spherical inspirals of spinning bodies into Kerr black holes”, Viktor Skoupý, Gabriel Andres Piovano, Vojtěch Witzany, arXiv:2506.20726
215. “Complete quasinormal modes of Type-D black holes”, Changkai Chen, Jiliang Jing, Zhoujian Cao, Mengjie Wang, arXiv:2506.14635
214. “Gravitational waves from b-EMRIs: Doppler shift and beaming, resonant excitation, helicity oscillations and self-lensing”, João S. Santos, Vitor Cardoso, José Natário, Maarten van de Meent, arXiv:2506.14868
213. “The Fast and the Frame-Dragging: Efficient waveforms for asymmetric-mass eccentric equatorial inspirals into rapidly-spinning black holes”, Christian E. A. Chapman-Bird, Lorenzo Speri, Zachary Nasipak, Ollie Burke, Michael L. Katz, Alessandro Santini, Shubham Kejriwal, Philip Lynch, Josh Mathews, Hassan Khalvati, Jonathan E. Thompson, Soichiro Isoyama, Scott A. Hughes, Niels Warburton, Alvin J. K. Chua, Maxime Pigou, arXiv:2506.09470 (*)
212. “Quasinormal modes in Kerr spacetime as a 2D Eigenvalue problem”, Jamil Assaad, Rodrigo Panosso Macedo, arXiv:2506.04326
211. “Self-force framework for merger-ringdown waveforms”, Lorenzo Küchler, Geoffrey Compère, Adam Pound arXiv:2506.02189
210. “Black hole spectroscopy: from theory to experiment”, Emanuele Berti et al. arXiv:2505.23895
209. “Resonant DM scattering in the galactic center under the influence of EMRI”, Takafumi Kakehi, Hidetoshi Omiya, Takuya Takahashi, Takahiro Tanaka, arXiv:2505.10036
208. “Universal Waveforms for Extreme Mass-Ratio Inspiral”, Ilan Strusberg, Barak Rom, Re’em Sari, arXiv:2505.07941
207. “Extreme mass ratio inspirals in rotating dark matter spikes”, Soumodeep Mitra, Nicholas Speeney, Sumanta Chakraborty, Emanuele Berti, arXiv:2505.04697
206. “Korteweg-de Vries Integrals for Modified Black Hole Potentials: Instabilities and other Questions”, Michele Lenzi, Arnau Montava Agudo, Carlos F. Sopuerta, arXiv:2503.09918
205. “Superconvergent Discontinuous Galerkin Method for the Scalar Teukolsky Equation on Hyperboloidal Domains: Efficient Waveform and Self-Force Computation”, Manas Vishal, Scott E. Field, Sigal Gottlieb, Jennifer Ryan, arXiv:2503.11523
204. “Quadratic quasinormal modes at null infinity on a Schwarzschild spacetime”, Patrick Bourg, Rodrigo Panosso Macedo, Andrew Spiers, Benjamin Leather, Bonga Béatrice, Adam Pound, arXiv:2503.07432
203. “Signatures of Quantum Gravity in Gravitational Wave Memory”, Nils Deppe, Lavinia Heisenberg, Lawrence E. Kidder, David Maibach, Sizheng Ma, Jordan Moxon, Kyle C. Nelli, William Throwe, Nils L. Vu, arXiv:2502.20584
202. “Fundamental Physics and Cosmology with TianQin”, Jun Luo et al. arXiv:2502.20138
201. “Parametric solutions to the Kerr separatrix”, Tammy Ng, Edward Teo, arXiv:2502.18141
200. “Lensing and wave optics in the strong field of a black hole”, Juno C. L. Chan, Conor Dyson, Matilde Garcia, Jaime Redondo-Yuste, Luka Vujeva, arXiv:2502.14073
199. “Approach to the separatrix with eccentric orbits”, Guillaume Lhost, Geoffrey Compère, arXiv:2412.04249
198. “Quantum Criticality in Black Hole Scattering”, Uri Kol, arXiv:2411.09814
197. “Renormalized charged scalar current on a Reissner-Nordstrom black hole in the presence of charge superradiance”, George Montagnon, Elizabeth Winstanley, arXiv:2501.10780
196. “Quantum-Corrected Hawking Radiation from Near-Extremal Kerr-Newman Black Holes”, Sabyasachi Maulik, Xin Meng, Leopoldo A. Pando Zayas, arXiv:2501.08252
195. “Resumming Post-Minkowskian and Post-Newtonian gravitational waveform expansions”, Andrea Cipriani, Giorgio Di Russo, Francesco Fucito, José Francisco Morales, Hasmik Poghosyan, Rubik Poghossian, arXiv:2501.19257
194. “Environmental effects in extreme mass ratio inspirals: perturbations to the environment in Kerr”, Conor Dyson, Thomas F.M. Spieksma, Richard Brito, Maarten van de Meent, Sam Dolan, arXiv:2501.09806
193. “Monodromy eigenvalues of the radial Teukolsky equation and their connection to the renormalized angular momentum”, Zachary Nasipak, arXiv:2412.06503
192. “Post-adiabatic waveform-generation framework for asymmetric precessing binaries”, Josh Mathews, Adam Pound, arXiv:2501.01413
191. “Ringdown of a postinnermost stable circular orbit of a rapidly spinning black hole: Mass ratio dependence of higher harmonic quasinormal mode excitation”, Daiki Watarai, arXiv:2408.16747
190. “Analytic solution for the motion of spinning particles in Kerr space-time”, Viktor Skoupý, Vojtěch Witzany, arXiv:2411.16855
189. “Gravitational self-force with hyperboloidal slicing and spectral methods”, Benjamin Leather, arXiv:2411.14976
188. “Post-Newtonian expansion of energy and angular momentum fluxes: inclined spherical orbits about a Kerr black hole”, Jezreel C. Castillo, Charles R. Evans, Chris Kavanagh, Jakob Neef, Adrian Ottewill, Barry Wardell, arXiv:2411.09700 (*)
187. “A note on the conversion of orbital angles for extreme mass ratio inspirals”, Philip Lynch, Ollie Burke, arXiv:2411.04955 (*)
186. “Gravitational memory: new results from post-Newtonian and self-force theory”, Kevin Cunningham, Chris Kavanagh, Adam Pound, David Trestini, Niels Warburton, Jakob Neef, arXiv:2410.23950 (*)
185. “Mode-sum prescription for renormalized expectation values for a charged quantum scalar field on a charged black hole”, Cormac Breen, George Montagnon, Peter Taylor, Elizabeth Winstanley, arXiv:2410.18211
184. “Impact of relativistic waveforms in LISA’s science objectives with extreme-mass-ratio inspirals”, Hassan Khalvati, Alessandro Santini, Francisco Duque, Lorenzo Speri, Jonathan Gair, Huan Yang, Richard Brito, arXiv:2410.17310
183. “A test for LISA foreground Gaussianity and stationarity. II. Extreme mass-ratio inspirals”, Manuel Piarulli, Riccardo Buscicchio, Federico Pozzoli, Ollie Burke, Matteo Bonetti, Alberto Sesana, arXiv:2410.08862
182. “Spinning particles near Kerr black holes: Orbits and gravitational-wave fluxes through the Hamilton-Jacobi formalism”, Gabriel Andres Piovano, Christiana Pantelidou, Jake Mac Uilliam, Vojtěch Witzany, arXiv:2410.05769
181. “Gravitational Wave Astronomy With TianQin”, En-Kun Li et al. arXiv:2409.19665
180. “Floating orbits and energy extraction from magnetized Kerr black holes”, João S. Santos, Vítor Cardoso, José Natário, arXiv:2409.17225
179. “Spin wave optics for gravitational waves lensed by a Kerr black hole”, Kei-ichiro Kubota, Shun Arai, Hayato Motohashi, Shinji Mukohyama, arXiv:2408.03289
178. “Post-Newtonian observables for aligned-spin binaries to sixth order in spin from gravitational self-force and Compton amplitudes”, Yilber Fabian Bautista, Mohammed Khalil, Matteo Sergola, Chris Kavanagh, Justin Vines, arXiv:2408.01871
177. “Gravitational wave surrogate model for spinning, intermediate mass ratio binaries based on perturbation theory and numerical relativity”, Katie Rink, Ritesh Bachhar, Tousif Islam, Nur E. M. Rifat, Kevin Gonzalez-Quesada, Scott E. Field, Gaurav Khanna, Scott A. Hughes, Vijay Varma, arXiv:2407.18319
176. “Gravitational waves from black hole emission”, Tousif Islam, Gaurav Khanna, Steven L. Liebling, arXiv:2407.16989
175. “Phenomenology and origin of late-time tails in eccentric binary black hole mergers”, Tousif Islam, Guglielmo Faggioli, Gaurav Khanna, Scott E. Field, Maarten van de Meent, Alessandra Buonanno, arXiv:2407.04682
174. “Teukolsky equation for near-extremal black holes beyond general relativity: near-horizon analysis”, Pablo A. Cano, Marina David, arXiv:2407.02017
173. “Probing new fundamental fields with Extreme Mass Ratio Inspirals”, Chao Zhang, Yungui Gong, arXiv:2407.07449
172. “High-speed reconstruction of long-duration gravitational waves from extreme mass ratio inspirals using sparse dictionary learning”, Charles Badger, José A. Font, Mairi Sakellariadou, Alejandro Torres-Forné, arXiv:2407.02908
171. “Amplitudes and Polarizations of Quadratic Quasi-Normal Modes for a Schwarzschild Black Hole”, Bruno Bucciotti, Leonardo Juliano, Adrien Kuntz, Enrico Trincherini, arXiv:2406.14611
170. “Post-Newtonian expansions of extreme mass ratio inspirals of spinning bodies into Schwarzschild black holes”, Viktor Skoupý, Vojtěch Witzany, arXiv:2406.14291
169. “Sourced metric perturbations of Kerr spacetime in Lorenz gauge”, Barry Wardell, Chris Kavanagh, Sam R. Dolan, arXiv:2406.12510
168. “Testing eccentric corrections to the radiation-reaction force in the test-mass limit of effective-one-body models”, Guglielmo Faggioli, Maarten van de Meent, Alessandra Buonanno, Aldo Gamboa, Mohammed Khalil, Gaurav Khanna, arXiv:2405.19006
167. “Fast inspirals and the treatment of orbital resonances”, Philip Lynch, Vojtěch Witzany, Maarten van de Meent, Niels Warburton, arXiv:2405.21072
166. “Detecting the massive vector field with extreme mass-ratio inspirals”, Tieguang Zi, Chao Zhang, arXiv:2406.11724
165. “Gravitational wave fluxes on generic orbits in near-extreme Kerr spacetime: higher spin and large eccentricity”, Changkai Chen, Jiliang Jing, arXiv:2311.15295
164. “Black hole scattering near the transition to plunge: Self-force and resummation of post-Minkowskian theory”, Oliver Long, Christopher Whittall, Leor Barack, arXiv:2406.08363
163. “Probing fundamental physics with Extreme Mass Ratio Inspirals: a full Bayesian inference for scalar charge”, Lorenzo Speri, Susanna Barsanti, Andrea Maselli, Thomas P. Sotiriou, Niels Warburton, Maarten van de Meent, Alvin J. K. Chua, Ollie Burke, Jonathan Gair, arXiv:2406.07607
162. “KerrGeoPy: A Python Package for Computing Timelike Geodesics in Kerr Spacetime”, Seyong Park, Zachary Nasipak, arXiv:2406.01413
161. “Backreaction from quantum fluxes at the Kerr inner horizon”, Tyler McMaken, arXiv:2405.13221
160. “Self-force framework for transition-to-plunge waveforms”, Lorenzo Küchler, Geoffrey Compère, Leanne Durkan, Adam Pound, arXiv:2405.00170
159. “Implementation of a GHZ-Teukolsky puncture scheme for gravitational self-force calculations”, Patrick Bourg, Benjamin Leather, Marc Casals, Adam Pound, Barry Wardell, arXiv:2403.12634
158. “Worldtube excision method for intermediate-mass-ratio inspirals: self-consistent evolution in a scalar-charge model”, Nikolas A. Wittek, Adam Pound, Harald P. Pfeiffer, Leor Barack, arXiv:2403.08864
157. “Hawking radiation inside a rotating black hole”, Tyler McMaken, Andrew J. S. Hamilton, arXiv:2401.03098
156. “Conserved currents for Kerr and orthogonality of quasinormal modes”, Stephen R. Green, Stefan Hollands, Laura Sberna, Vahid Toomani, Peter Zimmerman, arXiv:2210.15935
155. “Relativistic aerodynamics of spinning black holes”, Conor Dyson, Jaime Redondo-Yuste, Maarten van de Meent, Vitor Cardoso, arXiv:2402.07981
154. “A Survey of Four Precessing Waveform Models for Binary Black Hole Systems”, Jake Mac Uilliam, Sarp Akcay, Jonathan E. Thompson, arXiv:2402.06781
153. “The excitation of quadratic quasinormal modes for Kerr black holes”, Sizheng Ma, Huan Yang, arXiv:2401.15516
152. “Mapping between black-hole perturbation theory and numerical relativity II: gravitational-wave momentum”, Tousif Islam, arXiv:2401.14532
151. “Building a bridge between comparable and extreme mass ratio black hole binaries: a single spin precessing model for the final state”, Maria de Lluc Planas, Joan Llobera-Querol, Sascha Husa, arXiv:2401.13342
150. “Extreme mass-ratio inspirals as probes of scalar fields: inclined circular orbits around Kerr black holes”, Matteo Della Rocca, Susanna Barsanti, Leonardo Gualtieri, Andrea Maselli, arXiv:2401.09542
149. “DiscoTEX: Discontinuous collocation and implicit-turned-explicit (IMTEX) integration symplectic, symmetric numerical algorithms with higher order jumps for differential equations with numerical black hole perturbation theory applications”, Lidia J. Gomes Da Silva, arXiv:2401.08758
148. “Testing gravity with Extreme-Mass-Ratio Inspirals”, Alejandro Cárdenas-Avendaño, Carlos F. Sopuerta, arXiv:2401.08085
147. “Detecting dark matter with extreme mass-ratio inspirals”, Chao Zhang, Guoyang Fu, Ning Dai, arXiv:2401.04467
146. “Black Hole Perturbation Theory Meets CFT2: Kerr Compton Amplitudes from Nekrasov-Shatashvili Functions”, Yilber Fabian Bautista, Giulio Bonelli, Cristoforo Iossa, Alessandro Tanzini, Zihan Zhou, arXiv:2312.05965
145. “Ringdown of a dynamical spacetime”, Jaime Redondo-Yuste, David Pereñiguez, Vitor Cardoso, arXiv:2312.04633
144. “Waveform Modelling for the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna”, LISA Consortium Waveform Working Group et al., arXiv:2311.01300
143. “BHPWAVE: An adiabatic gravitational waveform model for compact objects undergoing quasi-circular inspirals into rotating massive black holes”, Zachary Nasipak, arXiv:2310.19706
142. “Accuracy Requirements: Assessing the Importance of First Post-Adiabatic Terms for Small-Mass-Ratio Binaries”, Ollie Burke, Gabriel Andres Piovano, Niels Warburton, Phillip Lynch, Lorenzo Speri, Chris Kavanagh, Barry Wardell, Adam Pound, Leanne Durkan, Jeremy Miller, arXiv:2310.08927
141. “Extreme mass-ratio inspiral and waveforms for a spinning body into a Kerr black hole via osculating geodesics and near-identity transformations”, Lisa V. Drummond, Philip Lynch, Alexandra G. Hanselman, Devin R. Becker, Scott A. Hughes, arXiv:2310.08438
140. “Mapping between black-hole perturbation theory and numerical relativity: gravitational-wave energy flux”, Tousif Islam, arXiv:2310.05743
139. “Impacts of Gravitational-Wave Background from Supermassive Black Hole Binaries on the Detection of Compact Binaries by LISA”, Fan Huang, Yan-Chen Bi, Zhoujian Cao, Qing-Guo Huang, arXiv:2309.14045
138. “Adiabatic inspirals under electromagnetic radiation reaction on Kerr spacetime”, Ethan J German, Kevin Cunningham, Visakan Balakumar, Niels Warburton, Sam R Dolan, arXiv:2309.10028
137. “Gravitational radiation from a particle plunging into a Schwarzschild black hole: frequency-domain and semi-relativistic analyses”, Hector O. Silva, Giovanni Tambalo, Kostas Glampedakis, Kent Yagi, arXiv:2308.14823
136. “Analytic solutions for the motion of spinning particles near spherically symmetric black holes and exotic compact objects”, Vojtěch Witzany, Gabriel Andres Piovano, arXiv:2308.00021
135. “Detection of astrophysical gravitational wave sources by TianQin and LISA”, Alejandro Torres-Orjuela, Shun-Jia Huang, Zheng-Cheng Liang, Shuai Liu, Hai-Tian Wang, Chang-Qing Ye, Yi-Ming Hu, Jianwei Mei, arXiv:2307.16628
134. “Extreme mass-ratio inspirals into black holes surrounded by scalar clouds”, Richard Brito, Shreya Shah, arXiv:2307.16093
133. “Fast and Fourier: Extreme Mass Ratio Inspiral Waveforms in the Frequency Domain”, Lorenzo Speri, Michael L. Katz, Alvin J. K. Chua, Scott A. Hughes, Niels Warburton, Jonathan E. Thompson, Christian E. A. Chapman-Bird, Jonathan R. Gair, arXiv:2307.12585 (*)
132. “High-order post-Newtonian expansion of the generalized redshift invariant for eccentric-orbit, equatorial extreme-mass-ratio inspirals with a spinning primary”, Christopher Munna, arXiv:2307.11158 (*)
131. “Quasinormal modes of rotating black holes in higher-derivative gravity”, Pablo A. Cano, Kwinten Fransen, Thomas Hertog, Simon Maenaut, arXiv:2307.07431
130. “Strongly-Lensed Extreme Mass-ratio Inspirals”, Martina Toscani, Ollie Burke, Chang Liu, Nour Bou Zamel, Nicola Tamanini, Federico Pozzoli, arXiv:2307.06722
129. “Towards exponentially-convergent simulations of extreme-mass-ratio inspirals: A time-domain solver for the scalar Teukolsky equation with singular source terms”, Manas Vishal, Scott E. Field, Katherine Rink, Sigal Gottlieb, Gaurav Khanna, arXiv:2307.01349
128. “Second-order perturbations of the Schwarzschild spacetime: practical, covariant and gauge-invariant formalisms”, Andrew Spiers, Adam Pound, Barry Wardell, arXiv:2306.17847 (*)
127. “Applying the effective-source approach to frequency-domain self-force calculations for eccentric orbits”, Benjamin Leather, Niels Warburton, arXiv:2306.17221
126. “Recipes for computing radiation from a Kerr black hole using Generalized Sasaki-Nakamura formalism: I. Homogeneous solutions”, Rico K. L. Lo, arXiv:2306.16469
125. “Metric perturbations of Kerr spacetime in Lorenz gauge: Circular equatorial orbits”, Sam R. Dolan, Leanne Durkan, Chris Kavanagh, Barry Wardell, arXiv:2306.16459
124. “Importance of including higher signal harmonics in the modeling of extreme mass-ratio inspirals”, Chao Zhang, Ning Dai, Dicong Liang, arXiv:2306.13871
123. “Hyperboloidal discontinuous time-symmetric numerical algorithm with higher order jumps for gravitational self-force computations in the time domain”, Lidia J. Gomes Da Silva, Rodrigo Panosso Macedo, Jonathan E. Thompson, Juan A. Valiente Kroon, Leanne Durkan, Oliver Long, arXiv:2306.13153
122. “Tidal heating and torquing of the primary black hole in eccentric-orbit, non-spinning extreme-mass-ratio inspirals to 22PN order”, Christopher Munna, Charles R. Evans, Erik Forseth, arXiv:2306.12481 (*)
121. “Gravitational waves from extreme mass ratio inspirals around a hairy Kerr black hole”, Tieguang Zi, Peng-Cheng Li, arXiv:2306.02683
120. “Self-forced inspirals with spin-orbit precession”, Philip Lynch, Maarten van de Meent, Niels Warburton, arXiv:2305.10533
119. “Frequency-domain approach to self-force in hyperbolic scattering”, Christopher Whittall, Leor Barack, arXiv:2305.09724
118. “Extreme mass-ratio inspiral of a spinning body into a Kerr black hole I: Evolution along generic trajectories”, Lisa V. Drummond, Alexandra G. Hanselman, Devin R. Becker, Scott A. Hughes, arXiv:2305.08919
117. “Gravitational Wave Peeps from EMRIs and their Implication for LISA Signal Confusion Noise”, Daniel J Oliver, Aaron D Johnson, Joel Berrier, Kostas Glampedakis, Daniel Kennefick, arXiv:2305.05793
116. “Detecting the secondary spin with extreme mass ratio inspirals in Scalar-Tensor theory”, Hong Guo, Chao Zhang, Yunqi Liu, Rui-Hong Yue, Yungui Gong, Bin Wang, arXiv:2305.00652
115. “Comparison of post-Minkowskian and self-force expansions: Scattering in a scalar charge toy model”, Leor Barack, Zvi Bern, Enrico Herrmann, Oliver Long, Julio Parra-Martinez, Radu Roiban, Michael S. Ruf, Chia-Hsien Shen, Mikhail P. Solon, Fei Teng, Mao Zeng, arXiv:2304.09200
114. “Enhancing the SEOBNRv5 effective-one-body waveform model with second-order gravitational self-force fluxes”, Maarten van de Meent, Alessandra Buonanno, Deyan P. Mihaylov, Serguei Ossokine, Lorenzo Pompili, Niels Warburton, Adam Pound, Barry Wardell, Leanne Durkan, Jeremy Miller, arXiv:2303.18026
113. “Asymptotic gravitational-wave fluxes from a spinning test body on generic orbits around a Kerr black hole”, Viktor Skoupý, Georgios Lukes-Gerakopoulos, Lisa V. Drummond, Scott A. Hughes, arXiv:2303.16798
112. “Lensing of Vacuum Entanglement near Schwarzschild Black Holes”, João G. A. Caribé, Robert H. Jonsson, Marc Casals, Achim Kempf, Eduardo Martín-Martínez, arXiv:2303.01402
111. “Black holes surrounded by generic dark matter profiles: appearance and gravitational-wave emission”, Enzo Figueiredo, Andrea Maselli, Vitor Cardoso, arXiv:2303.08183
110. “Kerr-fully Diving into the Abyss: Analytic Solutions to Plunging Geodesics in Kerr”, Conor Dyson, Maarten van de Meent, arXiv:2302.03704 (*)
109. “Action-Angle formalism for extreme mass ratio inspirals in Kerr spacetime”, Morteza Kerachian, Lukáš Polcar, Viktor Skoupý, Christos Efthymiopoulos, Georgios Lukes-Gerakopoulos, arXiv:2301.08150
108. “Remnant black hole properties from numerical-relativity-informed perturbation theory and implications for waveform modelling”, Tousif Islam, Scott E. Field, Gaurav Khanna, arXiv:2301.07215
107. “Quasi-normal modes of non-separable perturbation equations: the scalar non-Kerr case”, Rajes Ghosh, Nicola Franchini, Sebastian H. Völkel, Enrico Barausse, arXiv:2303.00088
106. “Detecting vector charge with extreme mass ratio inspirals onto Kerr black holes”, Chao Zhang, Hong Guo, Yungui Gong, Bin Wang, arXiv:2301.05915
105. “Quasinormal Modes from Penrose Limits”, Kwinten Fransen, arXiv:2301.06999
104. “Rapid determination of LISA sensitivity to extreme mass ratio inspirals with machine learning”, Christian E. A. Chapman-Bird, Christopher P. L. Berry, Graham Woan, arXiv:2212.06166
103. “Gravitational wave from extreme mass-ratio inspirals as a probe of extra dimensions”, Mostafizur Rahman, Shailesh Kumar, Arpan Bhattacharyya, arXiv:2212.01404
102. “Expansions for semiclassical conformal blocks”, Bruno Carneiro da Cunha, João Paulo Cavalcante, arXiv:2211.03551
101. “Gravitational waves from eccentric extreme mass-ratio inspirals as probes of scalar fields”, Chao Zhang, Yungui Gong, Dicong Liang, Bin Wang, arXiv:2210.11121
100. “Gravitational waves from extreme-mass-ratio systems in astrophysical environments”, Vitor Cardoso, Kyriakos Destounis, Francisco Duque, Rodrigo Panosso Macedo, Andrea Maselli, arXiv:2210.01133
99. “Regularized Stable Kerr Black Hole: Cosmic Censorships, Shadow and Quasi-Normal Modes”, Rajes Ghosh, Mostafizur Rahman, Akash K Mishra, arXiv:2209.12291
98. “Self-force regularization of a point particle for generic orbits in Kerr spacetime: electromagnetic and gravitational cases”, Anna Heffernan, arXiv:2209.05450
97. “Self-force correction to the deflection angle in black-hole scattering: a scalar charge toy model”, Leor Barack, Oliver Long, arXiv:2209.03740
96. “Eccentric binary black holes: Comparing numerical relativity and small mass-ratio perturbation theory”, Antoni Ramos-Buades, Maarten van de Meent, Harald P. Pfeiffer, Hannes R. Rüter, Mark A. Scheel, Michael Boyle, Lawrence E. Kidder, arXiv:2209.03390
95. “Comparing second-order gravitational self-force and effective one body waveforms from inspiralling, quasi-circular and nonspinning black hole binaries II: the large-mass-ratio case”, Angelica Albertini, Alessandro Nagar, Adam Pound, Niels Warburton, Barry Wardell, Leanne Durkan, Jeremy Miller, arXiv:2208.02055
94. “Comparing second-order gravitational self-force, numerical relativity and effective one body waveforms from inspiralling, quasi-circular and nonspinning black hole binaries”, Angelica Albertini, Alessandro Nagar, Adam Pound, Niels Warburton, Barry Wardell, Leanne Durkan, Jeremy Miller, arXiv:2208.01049
93. “Collective filters: a new approach to analyze the gravitational-wave ringdown of binary black-hole mergers”, Sizheng Ma, Keefe Mitman, Ling Sun, Nils Deppe, François Hébert, Lawrence E. Kidder, Jordan Moxon, William Throwe, Nils L. Vu, Yanbei Chen, arXiv:2207.10870
92. “Measuring accretion-disk effects with gravitational waves from extreme mass ratio inspirals”, Lorenzo Speri, Andrea Antonelli, Laura Sberna, Stanislav Babak, Enrico Barausse, Jonathan R. Gair, Michael L. Katz, arXiv:2207.10086
91. “Extreme Love in the SPA: constraining the tidal deformability of supermassive objects with extreme mass ratio inspirals and semi-analytical, frequency-domain waveforms”, Gabriel Andres Piovano, Andrea Maselli, Paolo Pani, arXiv:2207.07452
90. “Post-geodesic corrections to the binding energy during the transition to plunge in numerical relativity simulations”, Sergi Navarro Albalat, Aaron Zimmerman, Matthew Giesler, Mark A. Scheel, arXiv:2207.04066
89. “Slow evolution of the metric perturbation due to a quasicircular inspiral into a Schwarzschild black hole”, Leanne Durkan, Niels Warburton, arXiv:2206.08179
88. “QuasinormalModes.jl: A Julia package for computing discrete eigenvalues of second order ODEs”, Lucas Timotheo Sanches, arXiv:2206.04747
87. “Post-Newtonian expansion of the spin-precession invariant for eccentric-orbit non-spinning extreme-mass-ratio inspirals to 9PN and e^16”, Christopher Munna, Charles R. Evans, arXiv:2206.04085 (*)
86. “Modeling transient resonances in extreme-mass-ratio inspirals”, Priti Gupta, Lorenzo Speri, Béatrice Bonga, Alvin J.K. Chua, Takahiro Tanaka, arXiv:2205.04808
85. “The impact of relativistic corrections on the detectability of dark-matter spikes with gravitational waves”, Nicholas Speeney, Andrea Antonelli, Vishal Baibhav, Emanuele Berti, arXiv:2204.12508
84. “Detecting electric charge with Extreme Mass Ratio Inspirals”, Chao Zhang, Yungui Gong, arXiv:2204.01972
83. “Surrogate model for gravitational wave signals from non-spinning, comparable- to large-mass-ratio black hole binaries built on black hole perturbation theory waveforms calibrated to numerical relativity”, Tousif Islam, Scott E. Field, Scott A. Hughes, Gaurav Khanna, Vijay Varma, Matthew Giesler, Mark A. Scheel, Lawrence E. Kidder, Harald P. Pfeiffer, arXiv:2204.01972 (*)
82. “High-order post-Newtonian expansion of the redshift invariant for eccentric-orbit non-spinning extreme-mass-ratio inspirals”, Christopher Munna, Charles R. Evans, arXiv:2203.13832
81. “Extreme mass-ratio inspirals as probes of scalar fields: eccentric equatorial orbits around Kerr black holes”, Susanna Barsanti, Nicola Franchini, Leonardo Gualtieri, Andrea Maselli, Thomas P. Sotiriou, arXiv:2203.05003
80. “Redshift factor and the small mass-ratio limit in binary black hole simulations”, Sergi Navarro Albalat, Aaron Zimmerman, Matthew Giesler, Mark A. Scheel, arXiv:2203.04893
79. “Hyperboloidal method for frequency-domain self-force calculations”, Rodrigo Panosso Macedo, Benjamin Leather, Niels Warburton, Barry Wardell, Anıl Zenginoğlu, arXiv:2202.01794
78. “Precisely computing bound orbits of spinning bodies around black holes II: Generic orbits”, Lisa V. Drummond, Scott A. Hughes, arXiv:2201.13335
77. “Precisely computing bound orbits of spinning bodies around black holes I: General framework and results for nearly equatorial orbits”, Lisa V. Drummond, Scott A. Hughes, arXiv:2201.13334
76. “Detection of scalar fields by Extreme Mass Ratio Inspirals with a Kerr black hole”, Hong Guo, Yunqi Liu, Chao Zhang, Yungui Gong, Wei-Liang Qian, Rui-Hong Yue, arXiv:2201.10748
75. “Adiabatic equatorial inspirals of a spinning body into a Kerr black hole”, Viktor Skoupý, Georgios Lukes-Gerakopoulos, arXiv:2201.07044
74. “On Detecting Equatorial Symmetry Breaking with LISA”, Kwinten Fransen, Daniel R. Mayerson, arXiv:2201.03569
73. “The prospect of distinguishing astrophysical objects with LISA”, Mostafizur Rahman, Arpan Bhattacharyya, arXiv:2112.13869
72. “Gravitational waveforms for compact binaries from second-order self-force theory”, Barry Wardell, Adam Pound, Niels Warburton, Jeremy Miller, Leanne Durkan, Alexandre Le Tiec, arXiv:2112.12265
71. “Adiabatic waveforms from extreme-mass-ratio inspirals: an analytical approach”, Soichiro Isoyama, Ryuichi Fujita, Alvin J. K. Chua, Hiroyuki Nakano, Adam Pound, Norichika Sago, arXiv:2111.05288
70. “Deformed Schwarzschild horizons in second-order perturbation theory: mass, geometry, and teleology”, Riccardo Bonetto, Adam Pound, Zeyd Sam, arXiv:2109.09514
69. “The Radial Action from Probe Amplitudes to All Orders”, Uri Kol, Donal O’connell, Ofri Telem, arXiv:2109.12092
68. “Detecting Subsolar-Mass Primordial Black Holes in Extreme Mass-Ratio Inspirals with LISA and Einstein Telescope”, Susanna Barsanti, Valerio De Luca, Andrea Maselli, Paolo Pani, arXiv:2109.02170
67. “Survey of gravitational wave memory in intermediate mass ratio binaries”, Tousif Islam, Scott E. Field, Gaurav Khanna, Niels Warburton, arXiv:2109.00754
66. “Highly eccentric EMRI waveforms via fast self-forced inspirals”, Jonathan McCart, Thomas Osburn, Justin Y. J. Burton, arXiv:2109.00056
65. “Tests for the existence of horizon through gravitational waves from a small binary in the vicinity of a massive object”, Yun Fang, Rong-Zhen Guo, Qing-Guo Huang, arXiv:2108.04511
64. Regularization of a scalar charged particle for generic orbits in Kerr spacetime, Anna Heffernan, arXiv:2107.14750 (*)
63. Gravitational-wave energy flux for compact binaries through second order in the mass ratio, Niels Warburton, Adam Pound, Barry Wardell, Jeremy Miller, Leanne Durkan, arXiv:2107.01298
62. Detecting new fundamental fields with LISA, Andrea Maselli, Nicola Franchini, Leonardo Gualtieri, Thomas P. Sotiriou, Susanna Barsanti, Paolo Pani, arXiv:2106.11325
61. Divergences in gravitational-wave emission and absorption from extreme mass ratio binaries, Enrico Barausse, Emanuele Berti, Vitor Cardoso, Scott A. Hughes, Gaurav Khanna, arXiv:2106.09721
60. Classification of radial Kerr geodesic motion, Geoffrey Compère, Yan Liu, Jiang Long, arXiv:2106.03141
59. Resonant self-force effects in extreme-mass-ratio binaries: A scalar model, Zachary Nasipak, Charles R. Evans, arXiv:2105.15188
58. Assessing the detectability of the secondary spin in extreme mass-ratio inspirals with fully-relativistic numerical waveforms, Gabriel Andres Piovano, Richard Brito, Andrea Maselli, Paolo Pani, arXiv:2105.07083
57. Time-domain metric reconstruction for hyperbolic scattering, Oliver Long, Leor Barack, arXiv:2105.05630
56. Black-Hole Perturbation Plus Post-Newtonian Theory: Hybrid Waveform for Neutron Star Binaries, Xuefeng Feng, Zhenwei Lyu, Huan Yang, arXiv:2104.11848
55. FastEMRIWaveforms: New tools for millihertz gravitational-wave data analysis, Michael L. Katz, Alvin J.K. Chua, Lorenzo Speri, Niels Warburton, Scott A. Hughes, arXiv:2104.04582 (*)
54. Importance of tidal resonances in extreme-mass-ratio inspirals, Priti Gupta, Béatrice Bonga, Alvin J. K. Chua, Takahiro Tanaka, arXiv:2104.03422
53. Assessing the impact of transient orbital resonances, Lorenzo Speri, Jonathan R. Gair, arXiv:2103.06306
52. Stellar transits across a magnetized accretion torus as a mechanism for plasmoid ejection, Petra Suková, Michal Zajaček, Vojtěch Witzany, Vladimír Karas, arXiv:2102.08135
51. The Teukolsky-Starobinsky constants: facts and fictions, Rita Teixeira da Costa, Marc Casals, arXiv:2102.06734
50. “Spinning test body orbiting around a Kerr black hole: eccentric equatorial orbits and their asymptotic gravitational-wave fluxes”, Viktor Skoupý, Georgios Lukes-Gerakopoulos, arXiv:2102.04819
49. “Scope out multiband gravitational-wave observations of GW190521-like binary black holes with space gravitational wave antenna B-DECIGO”, Hiroyuki Nakano, Ryuichi Fujita, Soichiro Isoyama, Norichika Sago, arXiv:2101.06402
48. “Black hole perturbation theory and gravitational self-force”, Adam Pound, Barry Wardell, arXiv:2101.04592
47. “Gravitational wave templates from Extreme Mass Ratio Inspirals”, Viktor Skoupý, Georgios Lukes-Gerakopoulos, arXiv:2101.04533
46. “Post-Newtonian templates for gravitational waves from compact binary inspirals”, Soichiro Isoyama, Riccardo Sturani, Hiroyuki Nakano, arXiv:2012.01350
45. “Characteristic formulation of the Regge-Wheeler and Zerilli Green functions”, Conor O’Toole, Adrian Ottewill, Barry Wardell, arXiv:2010.15818
44. “Extreme precision for extreme spin: probing near-extremal black holes using LISA”, Ollie Burke, Jonathan R. Gair, Joan Simón, Matthew C. Edwards, arXiv:2010.05932
43. “Extreme mass ratio inspirals on the equatorial plane in the adiabatic order”, Ryuichi Fujita, Masaru Shibata, arXiv:2008.13554
42. “Electromagnetic self-force on a charged particle on Kerr spacetime: equatorial circular orbits”, T. Torres, S. R. Dolan, arXiv:2008.12703 (*)
41. “Augmented analytic kludge waveform with quadrupole moment correction”, Miaoxin Liu, Jian-dong Zhang, arXiv:2008.11396
40. “Analytic post-Newtonian expansion of the energy and angular momentum radiated to infinity by eccentric-orbit non-spinning extreme-mass-ratio inspirals to 19PN”, Christopher Munna, arXiv:2008.10622 (*)
39. “Rapid generation of fully relativistic extreme-mass-ratio-inspiral waveform templates for LISA data analysis”, Alvin J. K. Chua, Michael L. Katz, Niels Warburton, Scott A. Hughes, arXiv:2008.06071 (*)
38. “An alternative to the Teukolsky equation”, Yasuyuki Hatsuda, arXiv:2007.07906
37. “Intermediate mass-ratio black hole binaries: Applicability of small mass-ratio perturbation theory”, Maarten van de Meent, Harald P. Pfeiffer, arXiv:2006.12036
36. “Modeling and detecting resonant tides of exotic compact objects”, Kwinten Fransen, Gideon Koekoek, Rob Tielemans, Bert Vercnocke, arXiv:2005.12286,
35. “Ringing of rotating black holes in higher-derivative gravity”, Pablo A. Cano, Kwinten Fransen, Thomas Hertog, arXiv:2005.03671
34. “Determination of new coefficients in the angular momentum and energy fluxes at infinity to 9PN for eccentric Schwarzschild extreme-mass-ratio inspirals using mode-by-mode fitting”, Christopher Munna, Charles R. Evans, Seth Hopper, Erik Forseth, arXiv:2005.03044 (*)
33. “Pseudospectrum and black hole quasi-normal mode (in)stability”, José Luis Jaramillo, Rodrigo Panosso Macedo, Lamis Al Sheikh, arXiv:2004.06434
32. “Extreme mass ratio inspirals with spinning secondary: a detailed study of equatorial circular motion”, Gabriel Andres Piovano, Andrea Maselli, Paolo Pani1, arXiv:2004.02654 (*)
31. “Model independent tests of the Kerr bound with extreme mass ratio inspirals”, Gabriel Andres Piovano, Andrea Maselli, Paolo Pani, arXiv:2003.08448
30. “Redshift-space streaming velocity effects on the Lyman-α forest baryon acoustic oscillation scale”, Jahmour J. Givans, Christopher M. Hirata, arXiv:2002.12296
29. “Near-horizon geodesics of high-spin black holes”, Geoffrey Compère, Adrien Druart, arXiv:2001.03478 (*)
28. “Dissipation in extreme-mass ratio binaries with a spinning secondary”, Sarp Akcay, Sam R. Dolan, Chris Kavanagh, Jordan Moxon, Niels Warburton, Barry Wardell, arXiv:1912.09461 (*)
27. “The location of the last stable orbit in Kerr spacetime”, Leo C. Stein, Niels Warburton, arXiv:1912.07609 (*)
26. “A Surrogate Model for Gravitational Wave Signals from Comparable- to Large- Mass-Ratio Black Hole Binaries”, Nur E. M. Rifat, Scott E. Field, Gaurav Khanna, Vijay Varma, arXiv:1910.10473 (*)
25. “Spicing up the recipe for echoes from exotic compact objects: orbital differences and corrections in rotating backgrounds”, Luís Felipe Longo Micchi, Cecilia Chirenti, arXiv:1912.05419
24. “Gravitational wave signatures of ultralight vector bosons from black hole superradiance”, Nils Siemonsen, William E. East, Phys. Rev. D 101, 024019 (2020), arXiv:1910.09476
23. “Tidal heating as a discriminator for horizons in extreme mass ratio inspirals”, Sayak Datta, Richard Brito, Sukanta Bose, Paolo Pani, Scott A. Hughes, arXiv:1910.07841
22. “Gravitational Wave Perturbations on a Kerr Background and Applications for Echoes”, Randy S. Conklin, arXiv:1911.07122
21. “Regularized calculation of the retarded Green function in Schwarzschild spacetime”, Marc Casals, Brien C. Nolan, Adrian C. Ottewill, Barry Wardell, Phys. Rev. D 100, 104037 (2019), arXiv:1910.02567
20. “Transition from Inspiral to Plunge: A Complete Near-Extremal Waveform”, Ollie Burke, Jonathan R. Gair, Joan Simón, arXiv:1909.12846
19. “Eccentric-orbit EMRI radiation: Analytic forms of leading-logarithm and subleading-logarithm flux terms at high PN orders”, Christopher Munna, Charles R. Evans, arXiv:1909.05877 (*)
18. “Unveiling the Gravitational Universe at μ-Hz Frequencies”, Alberto Sesana et al. arXiv:1908.11391
17. “qnm: A Python package for calculating Kerr quasinormal modes, separation constants, and spherical-spheroidal mixing coefficients”, Leo C. Stein, J. Open Source Softw., 4(42), 1683 (2019) arXiv:1908.10377 (*)
16. “Factorization and resummation: A new paradigm to improve gravitational wave amplitudes. III: the spinning test-body terms”, Alessandro Nagar, Francesco Messina, Chris Kavanagh, Georgios Lukes-Gerakopoulos, Niels Warburton, Sebastiano Bernuzzi, Enno Harms, Phys. Rev. D 100, 104056 (2019), arXiv:1907.12233 (*)
15. “Quasi-circular inspirals and plunges from non-spinning effective-one-body Hamiltonians with gravitational self-force information”, Andrea Antonelli, Maarten van de Meent, Alessandra Buonanno, Jan Steinhoff, Justin Vines, arXiv:1907.11597
14. “Analytic solutions for parallel transport along generic bound geodesics in Kerr spacetime”, M. van de Meent, arXiv:1906.05090 (*)
13. “Repeated faint quasinormal bursts in EMRI waveforms: evidence from frequency-domain scalar self-force calculations on generic Kerr orbits”, Zach Nasipak, Thomas Osburn, Charles R. Evans, Phys. Rev. D 100, 064008 (2019), arXiv:1905.13237 (*)
12. “Hamilton-Jacobi equation for spinning particles near black holes”, Vojtěch Witzany, Phys. Rev. D 100, 104030 (2019), arXiv:1903.03651
11. “Gravitational waves from bodies orbiting the Galactic Center black hole and their detectability by LISA”, Eric Gourgoulhon, Alexandre Le Tiec, Frederic H. Vincent, Niels Warburton, A&A, 627 (2019) A92, arXiv:1903.02049 (*)
10. “Exciting black hole modes via misaligned coalescences: I. Inspiral, transition, and plunge trajectories using a generalized Ori-Thorne procedure”, Anuj Apte, Scott A. Hughes, Phys. Rev. D 100, 084031 (2019), arXiv:1901.05901
9. “Spin and Quadrupole Couplings for High Spin Equatorial Intermediate Mass-ratio Coalescences”, Bin Chen, Geoffrey Compère, Yan Liu, Jiang Long, Xuao Zhang, arXiv:1901.05370
8. “Spectroscopy of Extremal (and Near-Extremal) Kerr Black Holes”, M. Casals, Luís F. Longo Micchi, Phys. Rev. D 99, 084047 (2019), arXiv:1901.04586
7. “High-order asymptotics for the Spin-Weighted Spheroidal Equation at large real frequency”, M. Casals, A. C. Ottewill, N. Warburton, Proc. R. Soc. A 475:20180701 (2019), arXiv:1810.00432 (*)
6. ““Flux-balance formulae” for extreme mass-ratio inspirals”, Soichiro Isoyama, Ryuichi Fujita, Hiroyuki Nakano, Norichika Sago, Takahiro Tanaka, Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. (2019) 013E01, arXiv:1809.11118
5. “Gravitational self-force corrections to gyroscope precession along circular orbits in the Kerr spacetime”, D. Bini, T. Damour, A. Geralico, C. Kavanagh, M. van de Meent, Phys. Rev. D 98, 104062 (2018), arXiv:1809.02516 (*)
4. “Black holes, gravitational waves and fundamental physics: a roadmap”, Leor Barack et al., Class. Quant. Grav. 36:14 arXiv:1806.05195
3. “Fast Self-Forced Inspirals”, M. van de Meent, N. Warburton, Class. Quant. Grav. 35:144003, arXiv:1802.05281 (*)
2. “Gravitational waves from plunges into Gargantua”, Geoffrey Compère, Kwinten Fransen, Thomas Hertog, Jiang Long, Class. Quant.Grav. 35 (2018) no.10, 104002, arXiv:1712.07130
1. “Quantum correlator outside a Schwarzschild black hole”, Cláudia Buss, Marc Casals, Phys. Lett. B 776, p168-173 (2017), arXiv:1709.05990
If you have a work that makes use of the Toolkit and would like it listed here please let us know.